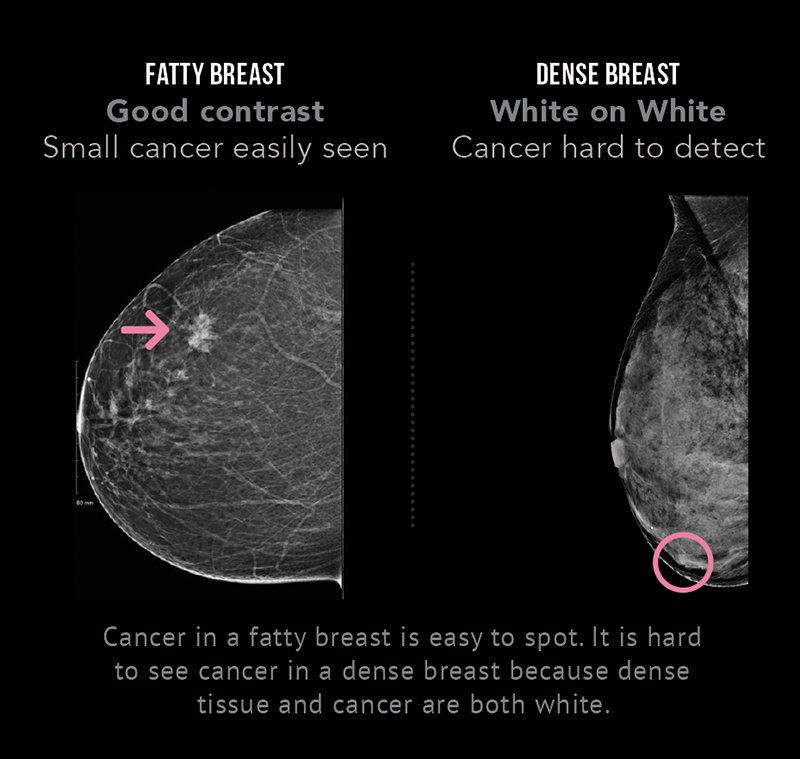
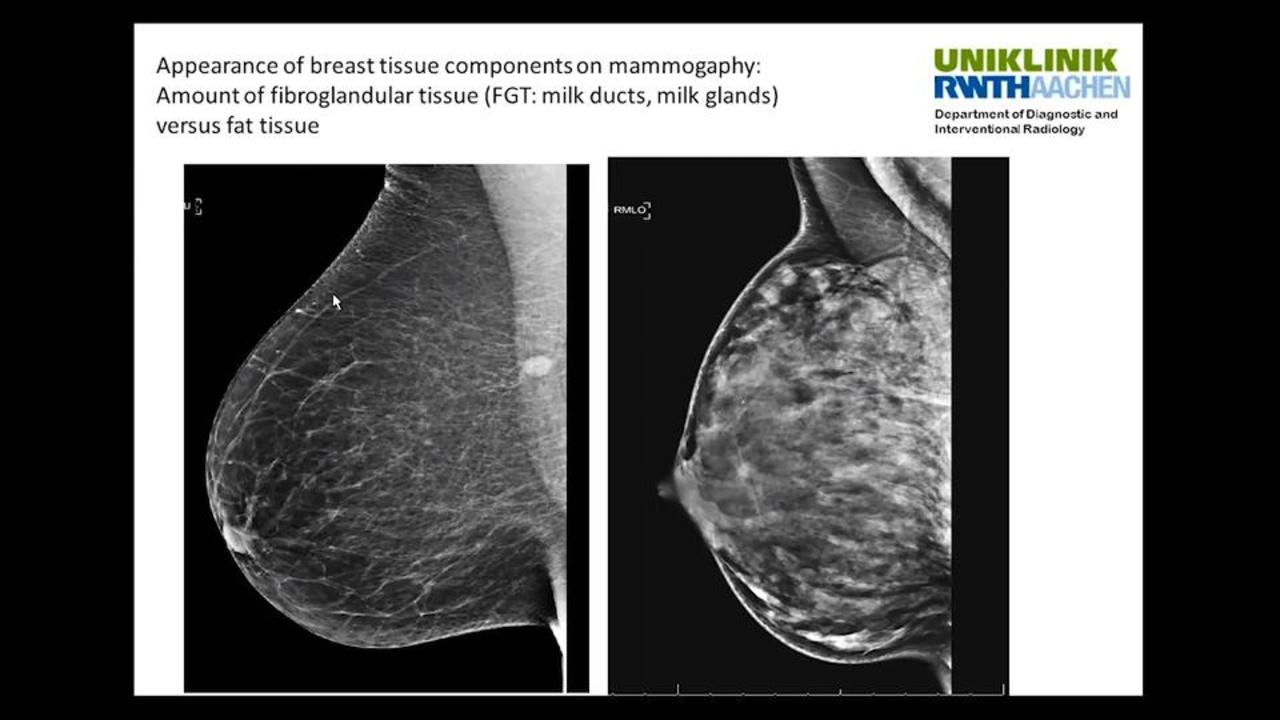
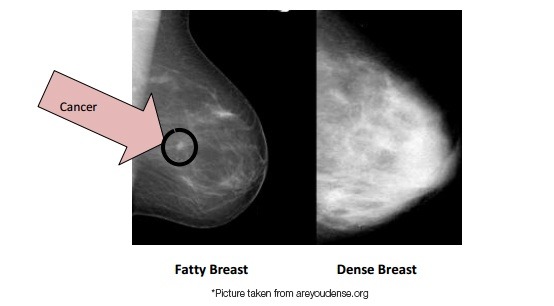
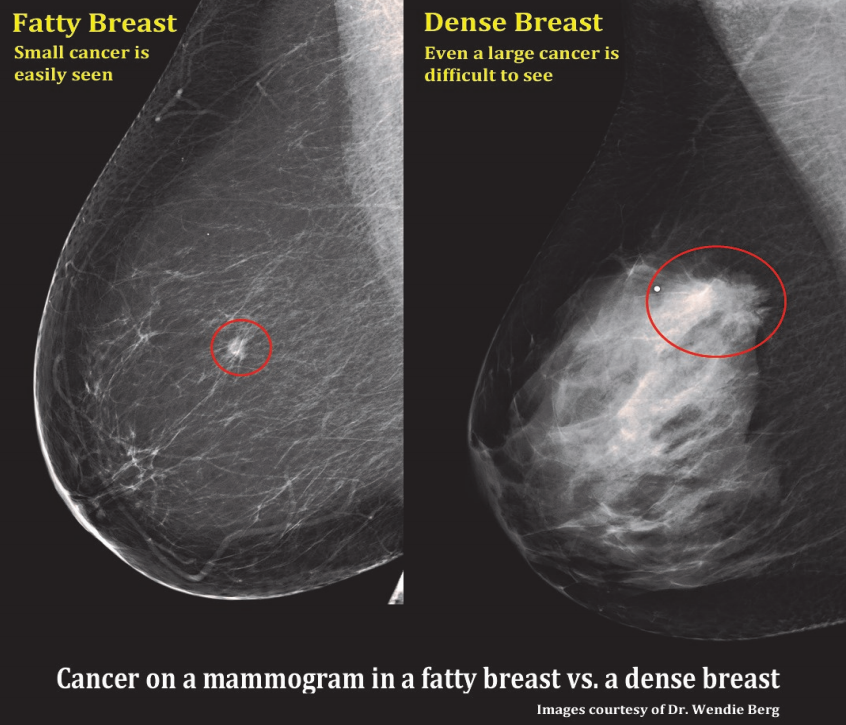
Calcifications are small deposits of calcium that show up on mammograms as bright white specks or dots on the soft tissue background of the breasts The calcium readily absorbs the Xrays from mammograms Calcifications typically don't show up on ultrasounds, and they never show up on breast MRIs Calcifications are a frequent finding onDense breast tissue is composed of less fat and more connective tissue, which appears white on Xray images created with mammography—the frontline tool of breast cancer screening Cancer also appears white on a mammogram, and if cancer is present, the tumors often are hidden behind the dense tissue Heterogeneously dense Most of the breast is dense tissue with some areas of fat Extremely dense The breasts have almost no fatty tissue
What Are Dense Breasts Does It Matter
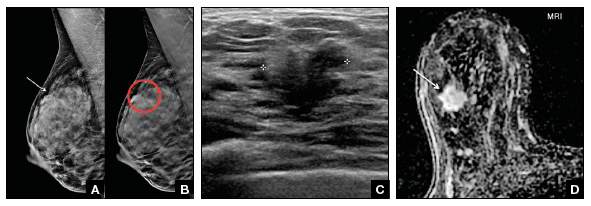
Heterogeneously dense breast tissue ultrasound
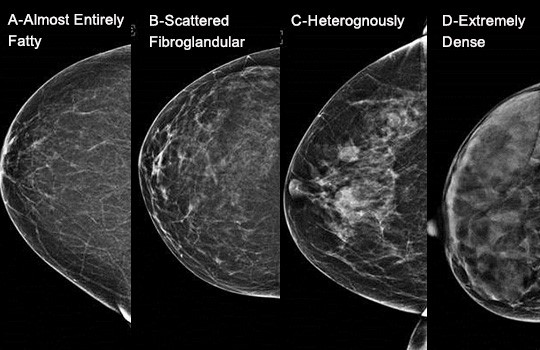
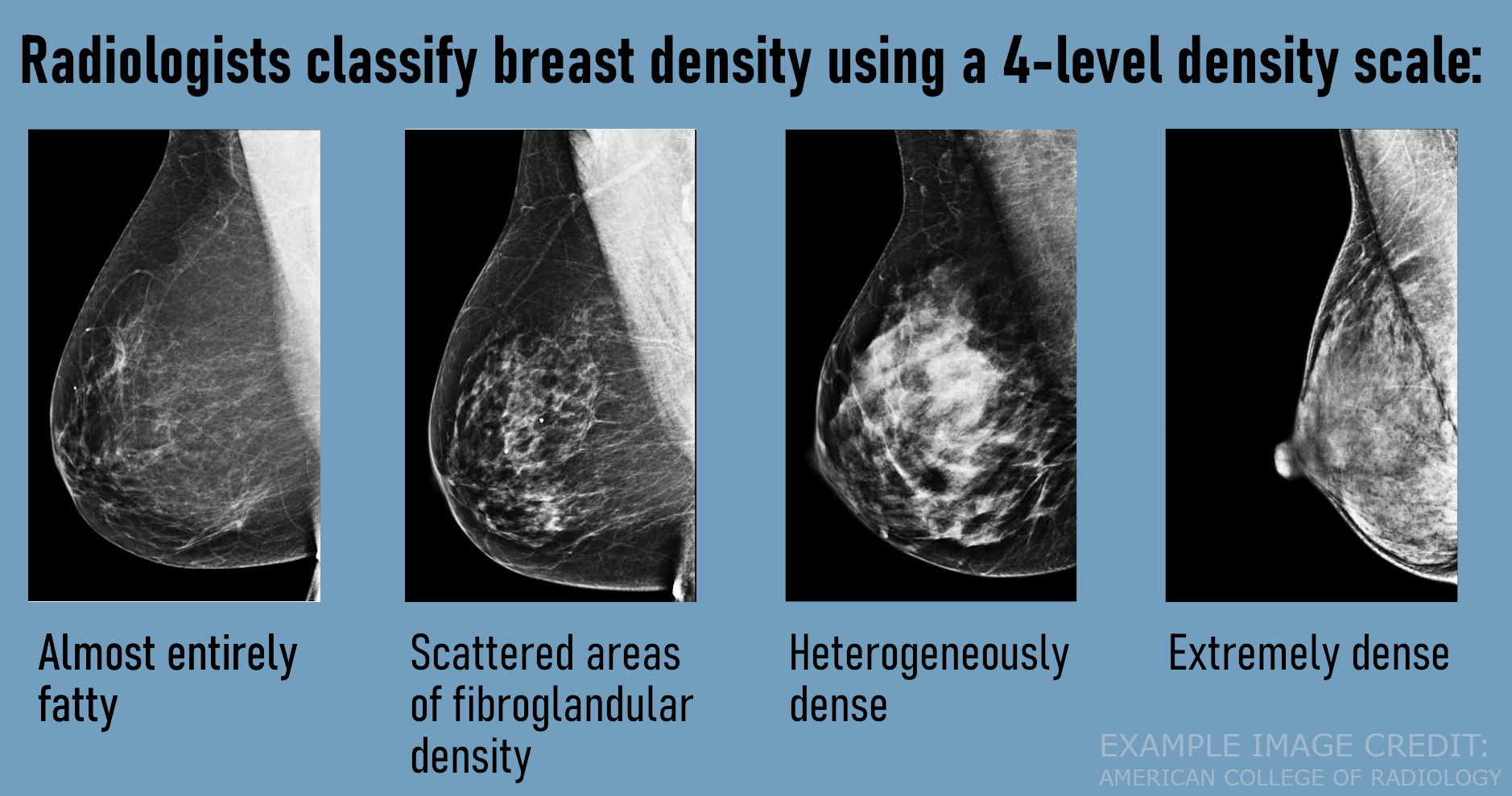
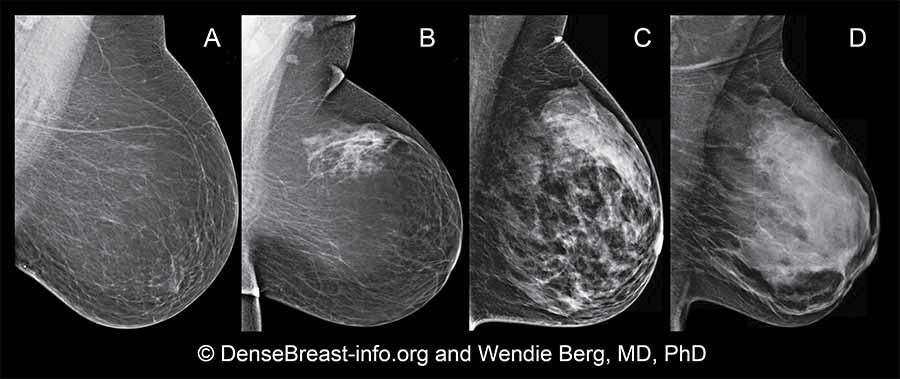
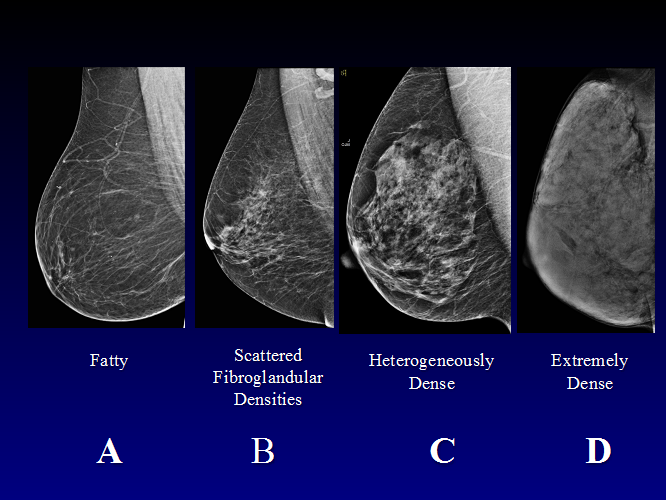
Heterogeneously dense breast tissue ultrasound- A primer of breast imaging modalities and how to keep patients informed Breast density is divided into four categories, from lowest to highest amounts of fibroglandular tissue composition Category A Almost entirely fatty (least amount of fibroglandular tissue) Category B Scattered fibroglandular tissue Category C Heterogeneously dense There are several risk factors associated with dense breast tissue, including Age A 18 study in the journal Cancer Epidemiology, Biomarkers and Prevention found that younger females tend to



What Breast Density Means To You Stacey Vitiello M D
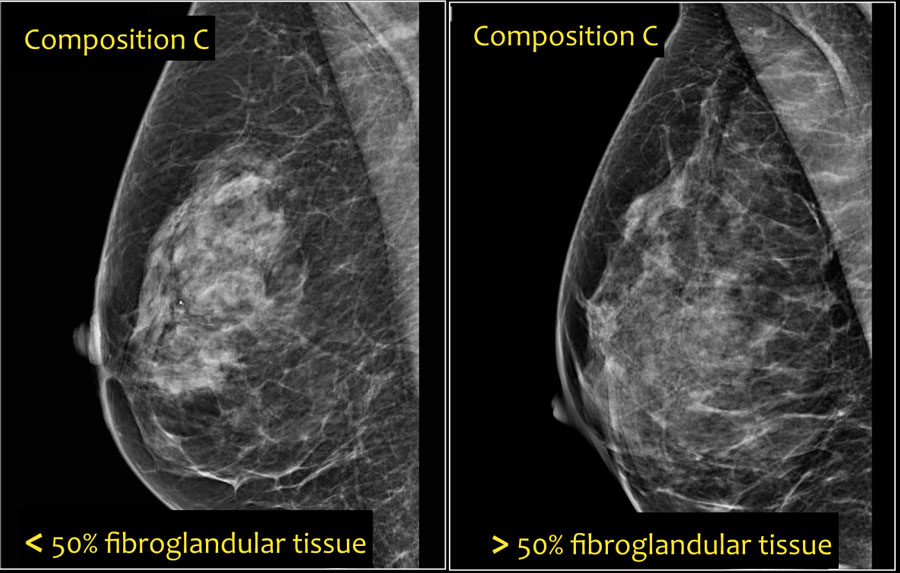
The breast tissue is heterogeneously dense, which could obscure detection of small masses (approximately 51% 75% glandular) 4 Heterogeneously Dense Breasts with Lots of Fibroglandular Tissue The term dense breasts is used to describe breast tissue that is less fatty and composed of more nonfatty ( fibrolandular) tissue than tissue found in breasts that are not dense Both researchers and doctors agree that women diagnosed with dense breasts are at a higher risk ofOnly about 10 percent of women are categorized as having extremely dense breast tissue You can learn more about these breast density types, and see images too, at the American Cancer Society Here at North Texas Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery,
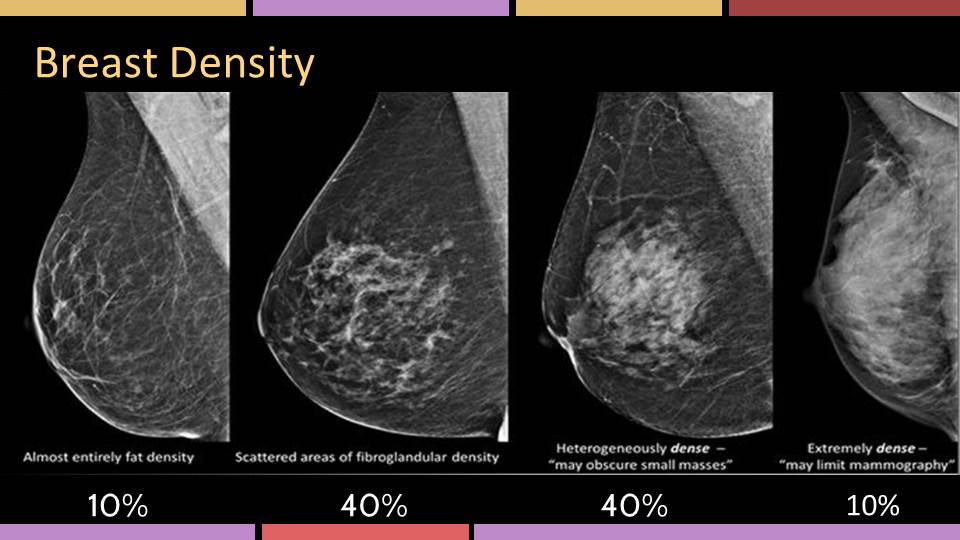
The breast tissue is heterogeneously dense, which may obscure small masses (40% of women) The breast tissue is extremely dense This may lower the sensitivity of mammography (10% of women) Approximately 50% of women undergoing screening mammography are classified as having either "heterogeneously dense" or "extremely dense" breasts Breast tissue Breast are made of milk ducts, supportive tissue and fatty tissue Women with dense breasts have a higher ratio of supportive tissue to fatty tissue Women with dense breasts have a higher ratio of supportive tissue to fatty tissueCertain diseases, such as breast cancer, can change the characteristics of the breast parenchyma Stroma is the scientific term for all of the tissue on the breast that is not part of the parenchyma This is the fatty and connective tissue that gives the breast volume, and also provides an essential blood supply to the parenchymal cells of the breast
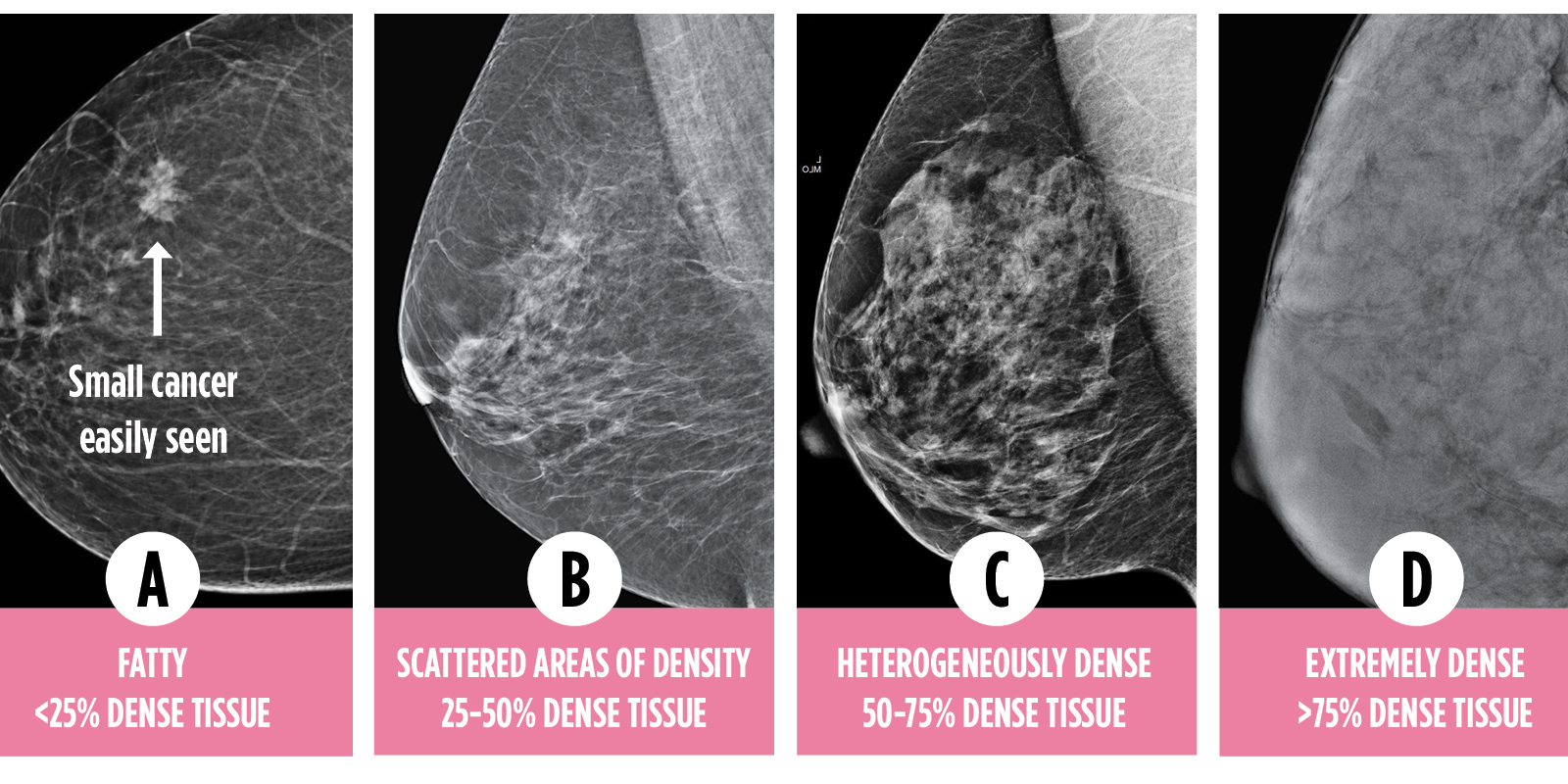
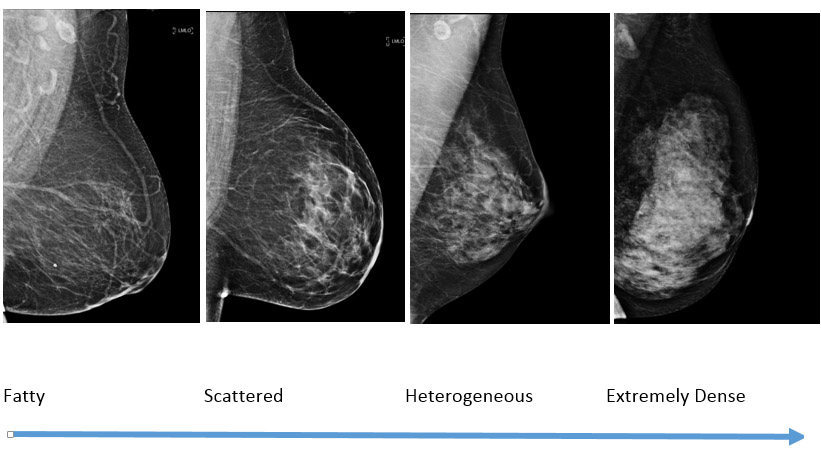
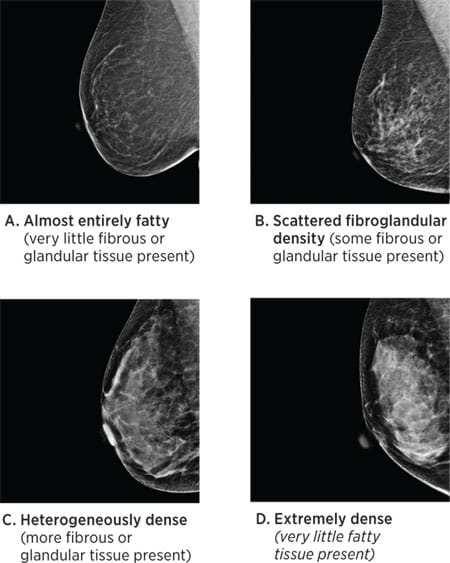
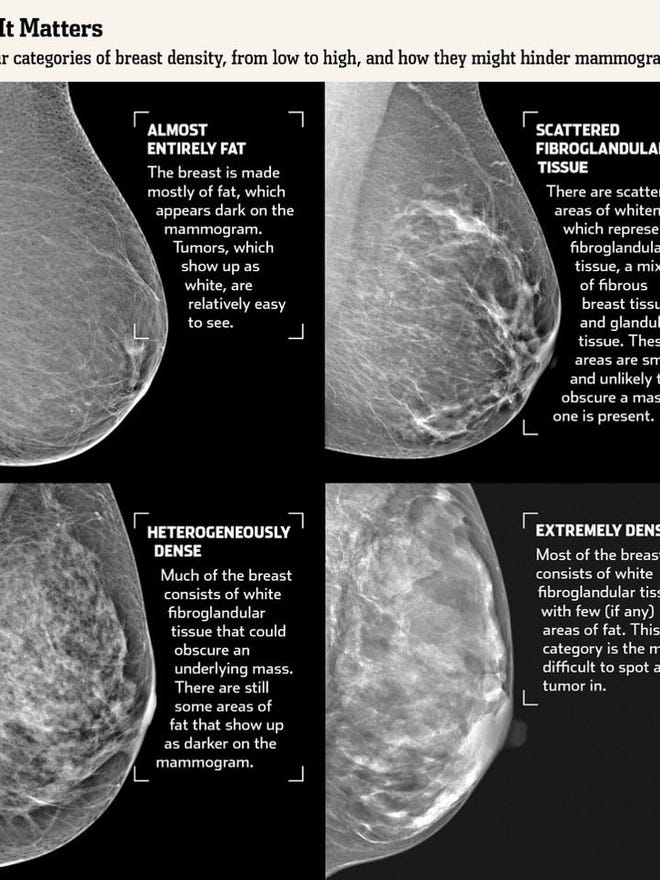
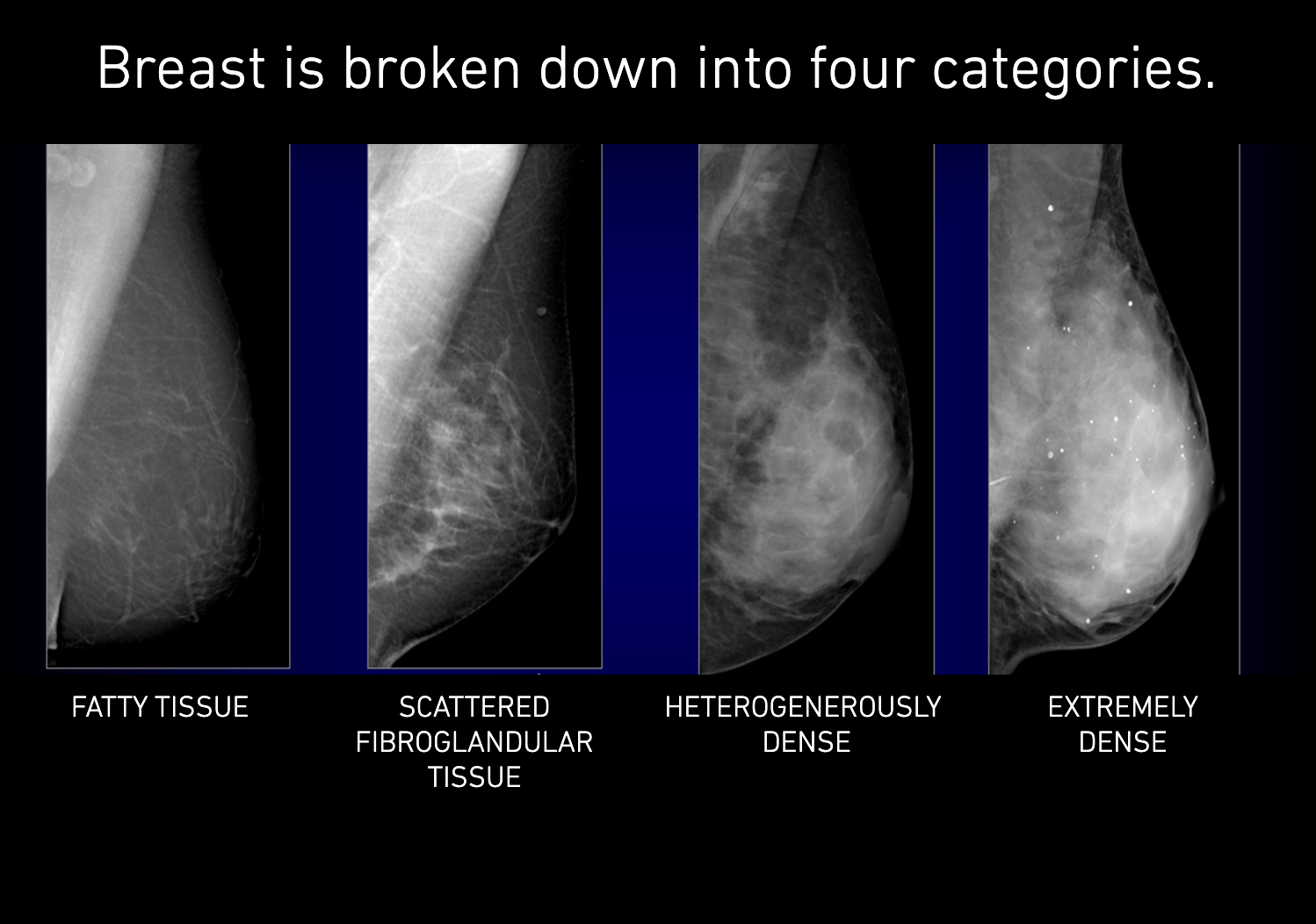
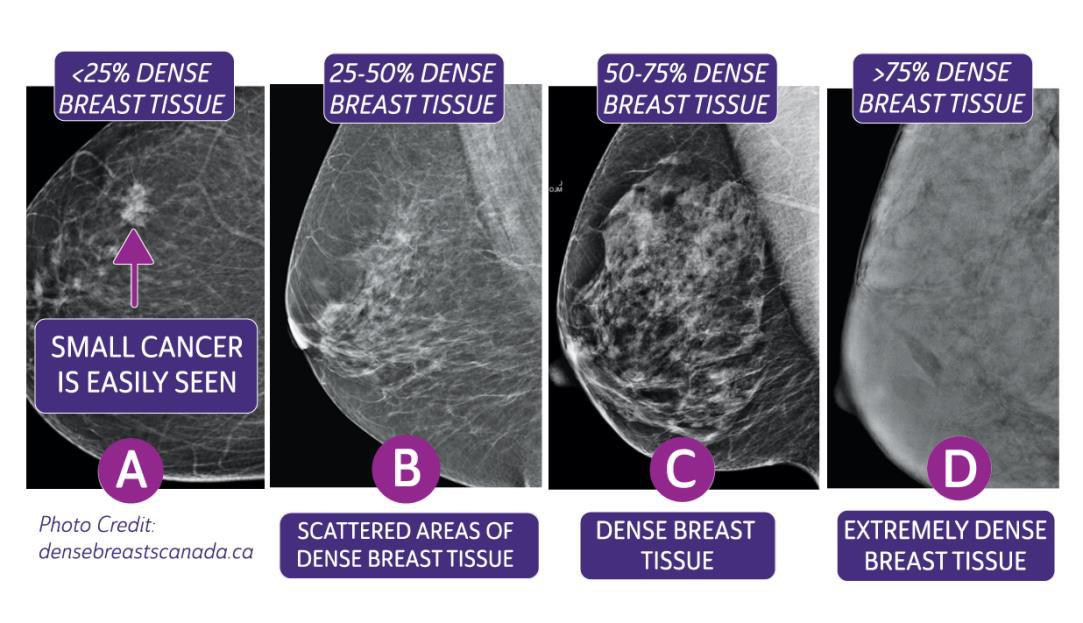
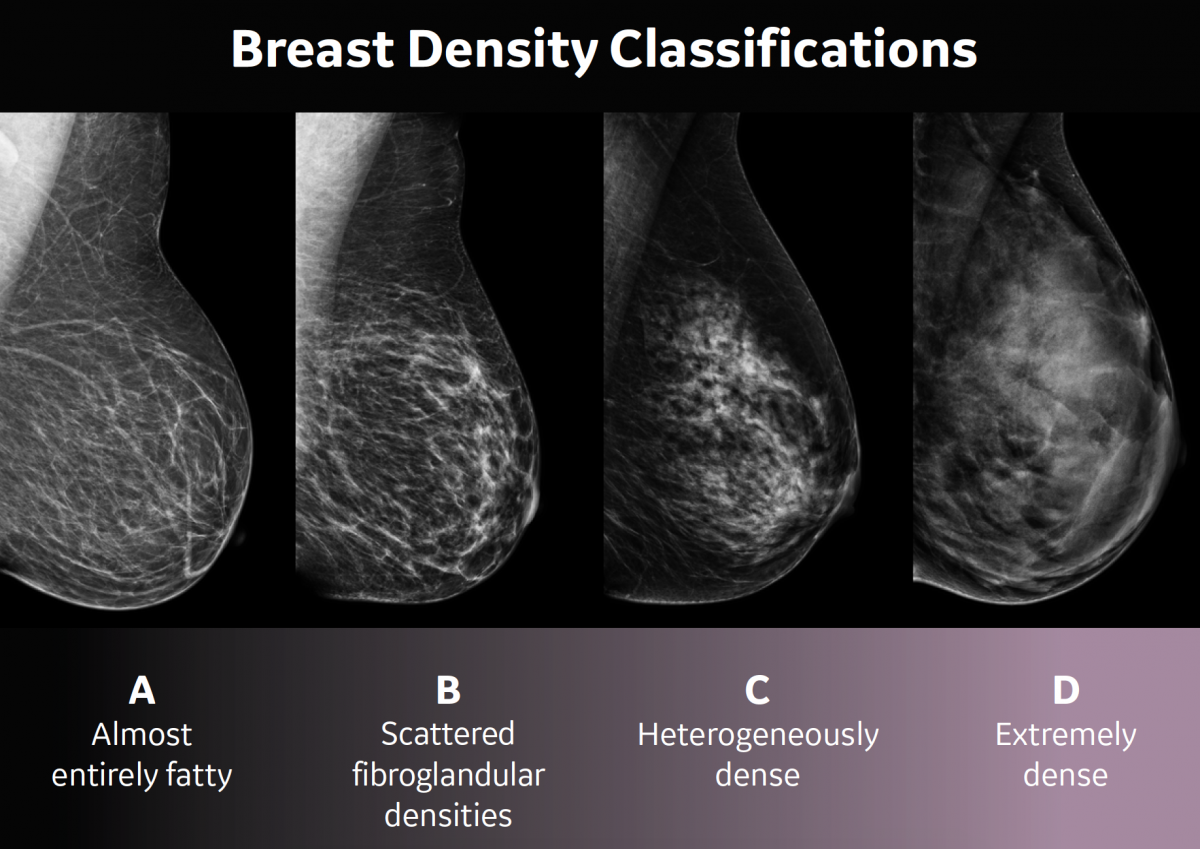
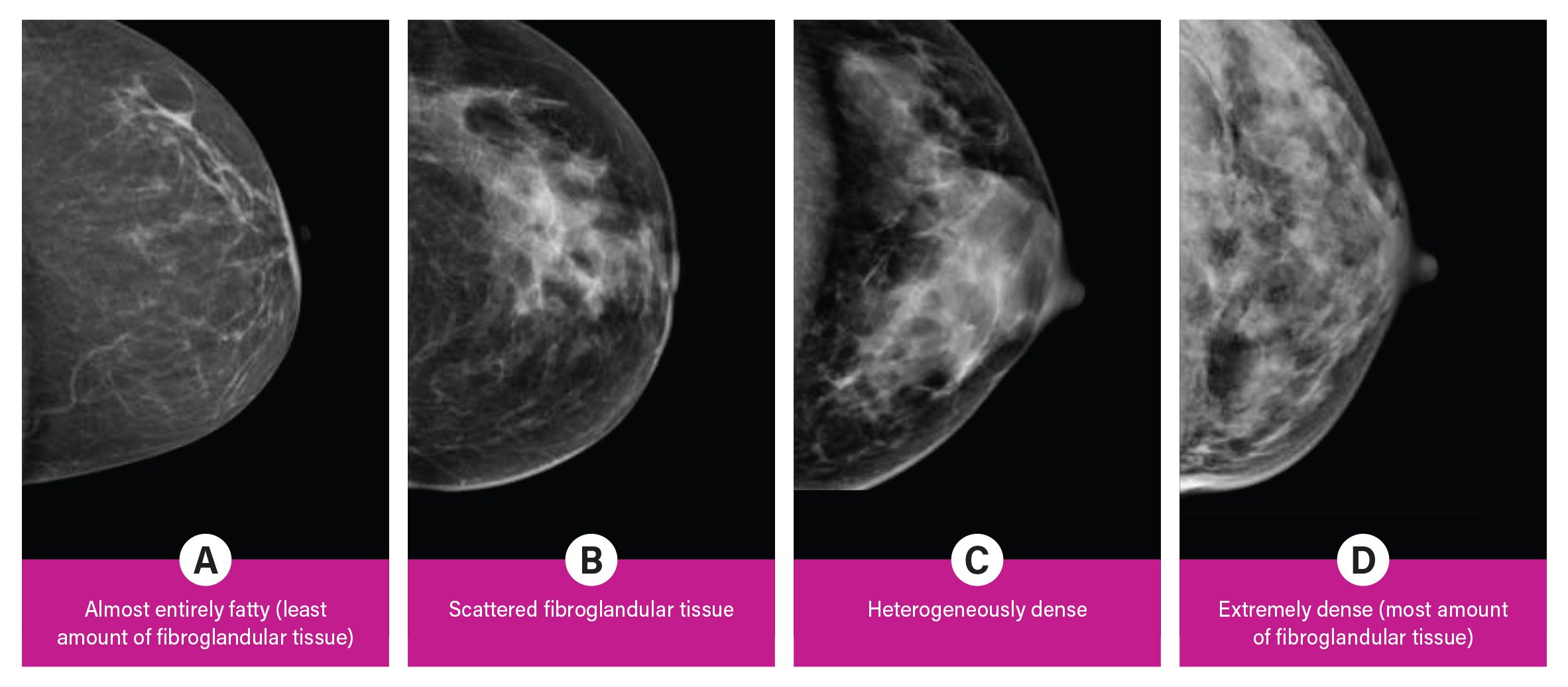
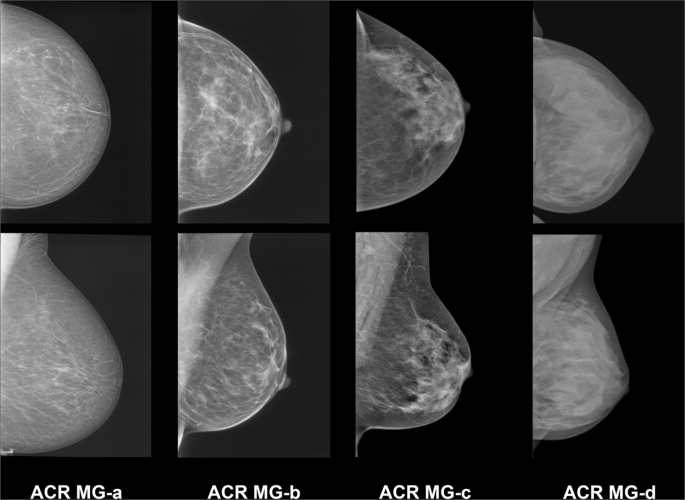
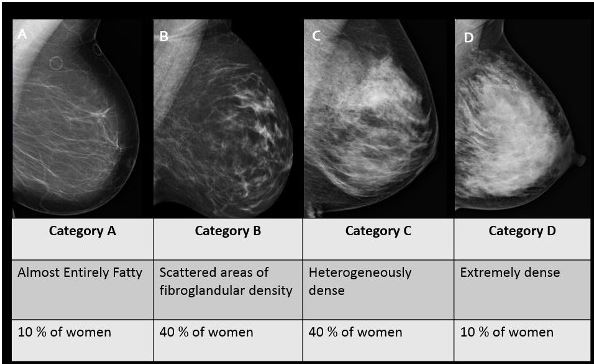
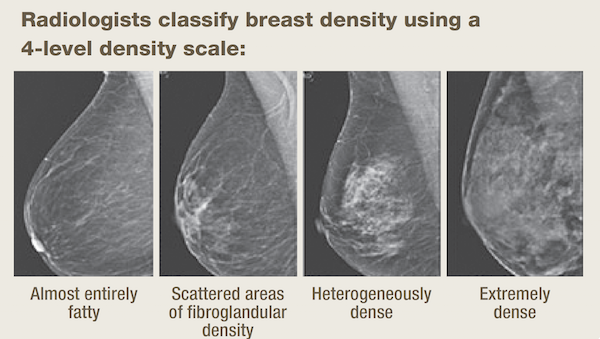
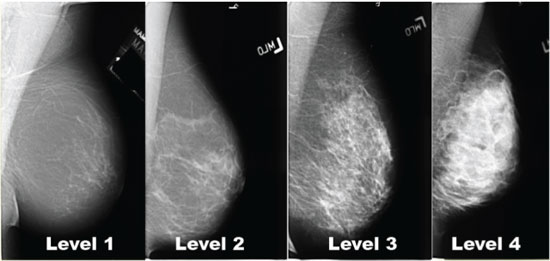
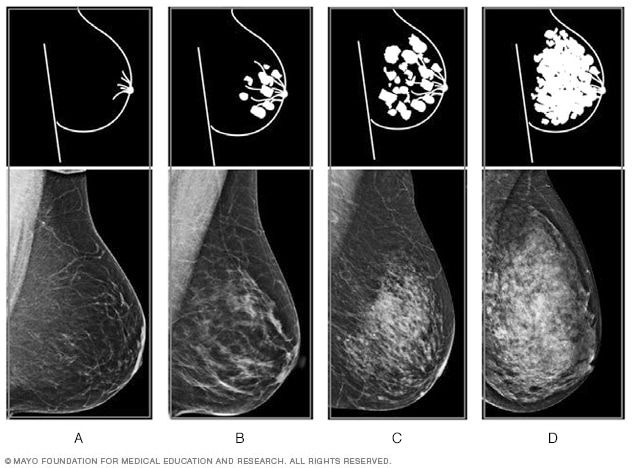
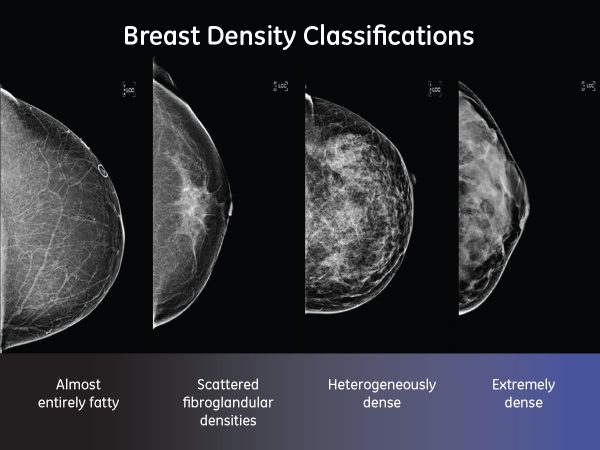
1— Breast tissue is almost entirely fat with less than 25 percent of the breast composed of glandular tissue 2 — Breast tissue contains scattered fibroglandular densities with between 25 and 50 percent of the breast composed of glandular tissue 3 — Breast tissue is heterogeneously dense with between 51 and 75 percent of the breast Fatty tissue is not muscle it's more fat Nondense means fatty tissue Heterogeneously dense has some areas of fatty tissue but most of the breast is dense Density levels are recorded in mammograms using letters AD A Almost entirely fatty meaning the breast are almost composed with fat This is usually found in 10% of womenIn fact, about half of all women over 40 have dense breasts
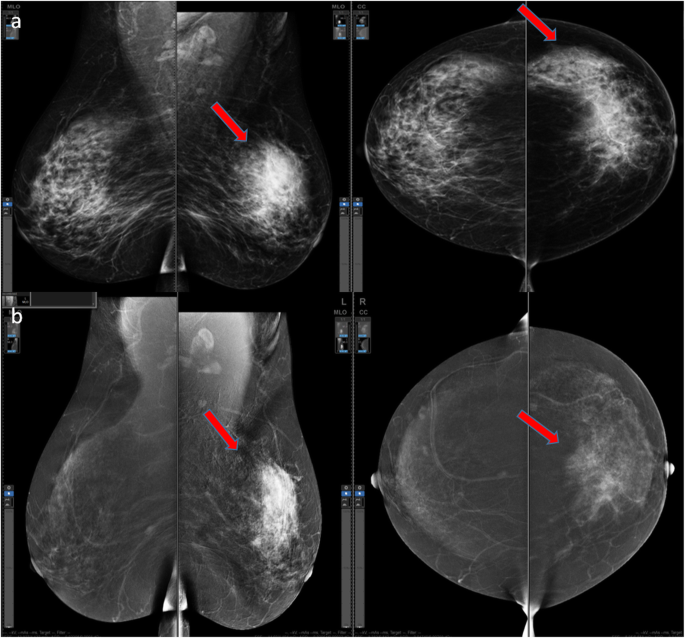



Does Contrast Enhanced Mammography Have An Impact On The Detection Of Cancer In Patients With Risk Of Developing Breast Cancer Springerlink



Get Informed Dense Breasts Canada Find Out Your Breast Density
Among women with dense breasts, the risk of developing an interval cancer was greatest in those with extremely dense breasts (at least 75 percent of breast tissue is dense) and a 5year risk of 167 percent or more and in those with heterogeneously dense breasts (more than half of the tissue in their breasts is dense) and a 5year risk of 25 percent or moreOther tissue in the breast is fat tissue "It is more common to have dense breast tissue when women are premenopausal Exposure to estrogen, like taking birth control pills, can also increase breast density" However, there are women with heterogeneously and even extremely dense breasts who have never taken birth control pills or estrogenDense tissue appears white on a mammogram;




Should You Worry About Dense Breasts Everyday Health




Breast Density Testing In Rochester Ny Elizabeth Wende Breast Care
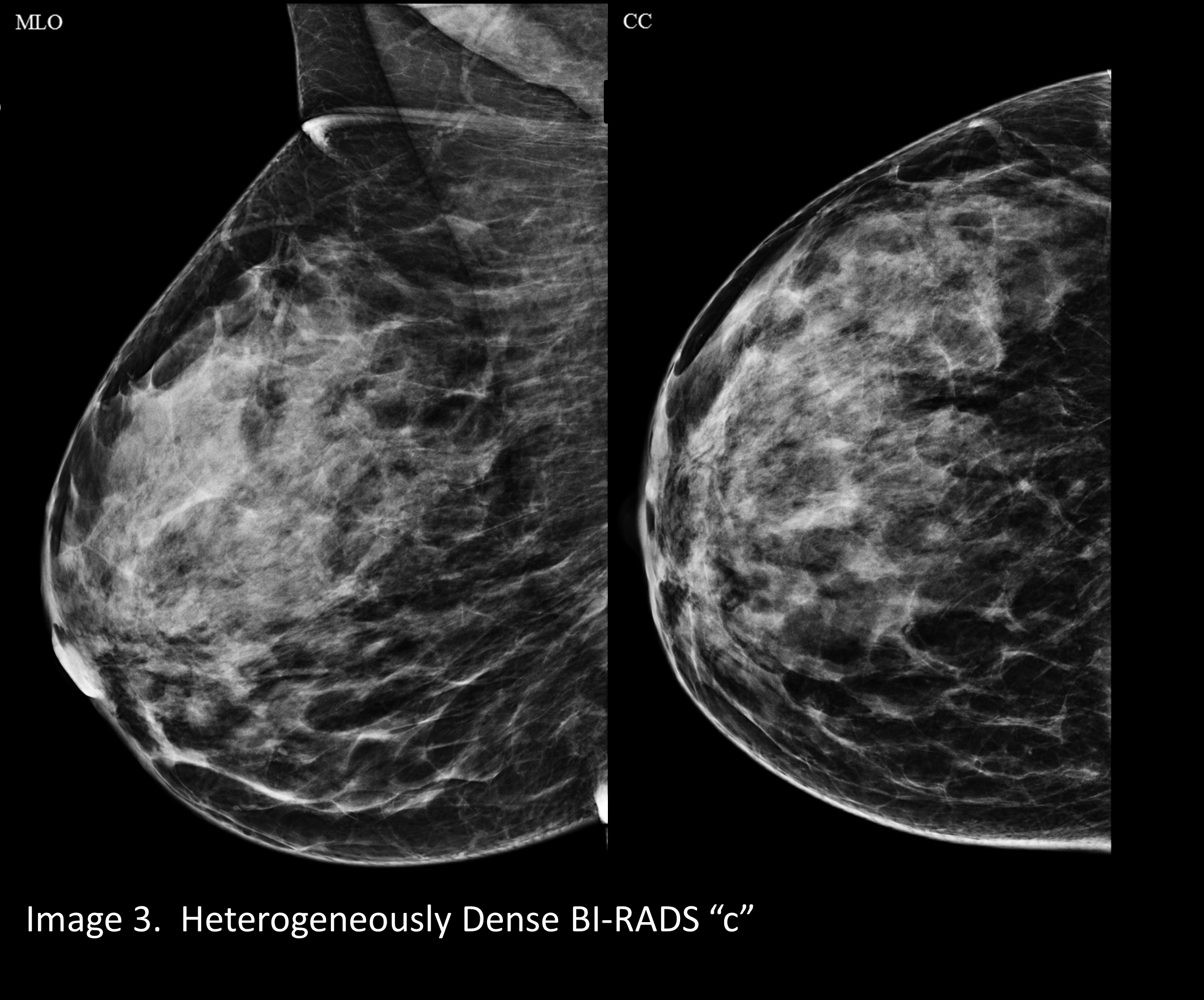
Breast density refers to the amount of glandular and fibrous tissue Dense breasts have mostly glandular tissue, with just a little fat tissue A woman's breast density can change through her life There are four types of breast density, from most to least dense Extremely dense Heterogeneously denseFibroglandular density refers to scattered areas of density in the breast, which is normal tissue seen in combination with fat My mammogram described my breasts as being "heterogeneously dense, which may obscure small masses" What does that mean?Moderately dense, heterogeneously dense, or extremely dense breast tissue, or if the patient has additional risk factors for breast cancer including but not limited to family history of breast cancer, prior personal history of breast cancer, positive genetic testing, extremely
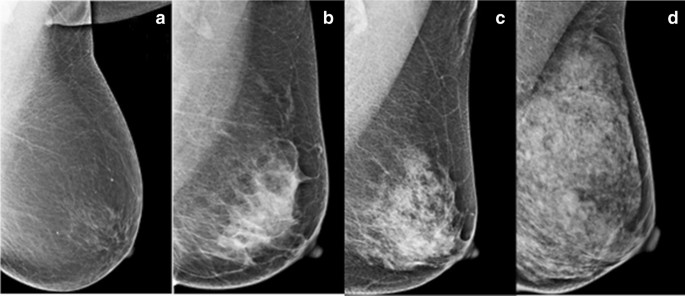



The Relationship Between Breast Density Age And Mammographic Lesion Type Among Chinese Breast Cancer Patients From A Large Clinical Dataset Bmc Medical Imaging Full Text




Breast Density Consulting Radiologists
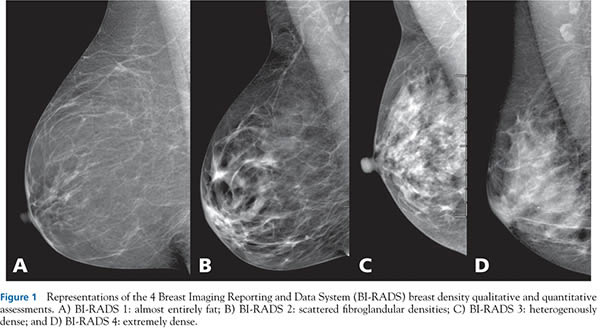
Specialists term the breast tissue in type 3 as 'heterogeneously dense' The parenchyma ranges from 51% to 75% of the breast tissue 'Heterogeneous' means something contains many different items and has many different variationsLumps, both benign and cancerous, also appear white So, mammograms can be less accurate in women with dense breasts If a woman's mammogram shows she has heterogeneously dense or extremely dense breast tissue, she will receive a letter notifying her that she has dense breastsThe categories are, (A) almost entirely fatty, (B) scattered fibroglandular density, heterogeneously dense, and (D) extremely dense On a mammogram, fatty and connective tissue shows up as a grey color and glandular tissue shows up as white – as do cancerous tumors



Breast Density Canadian Cancer Survivor Network



What Are Dense Breasts Does It Matter
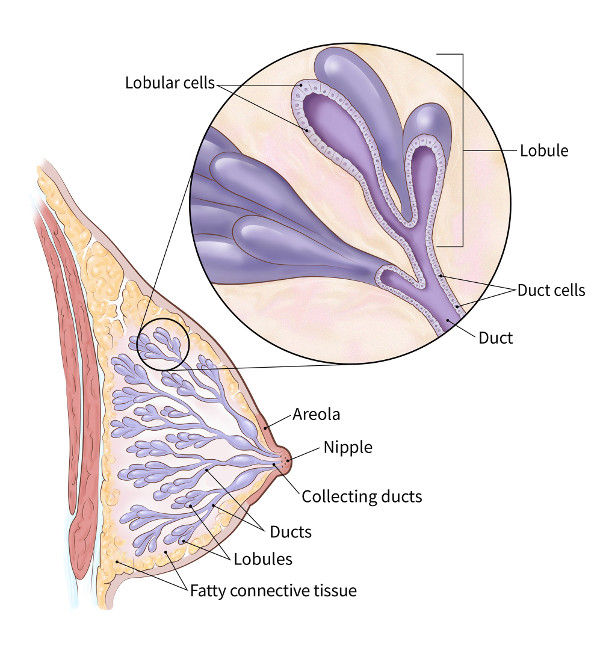
All breasts contain ducts and their milkproducing glands, fibrous tissue, and fat The glands and fibrous tissue (or "fibroglandular" tissue) are referred to as "dense tissue" Each woman's breasts are different from the next and contain a unique mix of fatty and dense tissueThis means that you have moderately dense tissue, which is common and not a cause for concernAccording to the National Cancer Institute, nearly 50% of all women age 40 and older have dense breasts Like Joan, many women don't know whether they have dense breasts or what that means Knowing whether you have dense breasts is important because women with dense breasts have a higher risk of developing breast cancer, and often need




Subject Dense Breasts Standard Of Care




Breast Density What S All The Fuss About The Medical Republic
Class D (or 4) Extremely dense How does breast tissue density affect a radiologist's ability to detect breast cancer?Low breast density means there is a greater amount of fat compared to breast and connective tissue Breast density and its relationship to estrogen is an important risk factor for diverse subtypes of breast cancer Check out how the "fickle" estrogen shows up in different ways, effecting breast density • Young women have more circulating Heterogeneously dense indicates that some areas of nondense tissue were found, but the majority of the breast tissue is dense About 40 percent women have this result Extremely dense indicates that nearly all the breast tissue is dense About 10



Breast Density Robert H Lurie Comprehensive Cancer Center Of Northwestern University Feinberg School Of Medicine Northwestern University




Dense Breasts Are You Educated Link
Radiologists use mammogram images to grade breast tissue based on the proportion of dense to nondense tissue According to the BIRADS reporting system, the levels are (from left to right) almost entirely fatty, scattered areas of fibroglandular density, heterogeneously dense and extremely dense Class C (or 3) Heterogeneously dense; "Comparing women with extremely dense breast tissue to those with fatty breasts, we find a four to six times increased risk for breast cancer Women with heterogeneously dense breasts have about



Dense Breast Clinic Cooper University Health Care




Breast Density What Is It And What Does It Mean For Me Breast360 Org The American Society Of Breast Surgeons Foundation
Dense breast tissue is a normal finding, and about half of all women have dense breast tissue If you have dense breast tissue, this means you have a higher proportion of glandular breast tissue to fatty tissue Having dense breast tissue can make it more difficult to see breast cancer on a mammogram Dense tissue appears white on a mammogramBIRADS classifies breast density into four categories, as follows (A) Almost entirely fatty breast tissue, found in about 10% of women (B) Scattered areas of dense glandular tissue and fibrous connective tissue ( scattered fibroglandular breast tissue) Heterogeneously dense breast tissue Scattered density – A breast has a fair amount of fat with a few areas of fibrous and glandular tissue Heterogeneously dense – A breast has more fibrous and glandular tissue This can make it more difficult for a radiologist to detect cancerous changes in a mammogram Extremely dense – A breast has a high amount of fibrous and glandular




Many Women With Dense Breasts May Not Need Additional Screening National Cancer Institute




Breast Density What Is It And What Does It Mean For Me Breast360 Org The American Society Of Breast Surgeons Foundation
Dense Breasts Breast density is a proportional measure of the glandular, connective and fatty tissues within a woman's breasts It is most commonly determined using mammography, a diagnostic test that uses low dose xrays Having dense breasts is not an abnormal condition; Women who have dense breast tissue, either heterogeneously dense or extremely dense, in addition to other risk factors for breast cancer may need additional breast cancer screening tests A simple Breast asymmetry is a common characteristic for women, and is often no cause for concern However, if the size of your breasts change or the density



Video Explaining Dense Breasts Imaging Technology News
%20.png)



What Is Breast Density And Why Does It Matter Our Voices Blog Cbcn
Heterogeneously dense breasts is a term used in mammography to describe breasts with a higher percentage of glandular and supportive tissue than fat It occurs in 40% of women and while normal, can make it more difficult to detect breast cancer on mammographyThe California legislature recently passed a law (SB 1538) requiring that women who have screening mammograms be informed if they have dense breast tissue Specifically, women who have dense breast tissue will receive the following statement in writing as part of their mammogram result "Your mammogram shows that your breast tissue is denseBreast density reflects the amount of fibrous and glandular tissue in a woman's breasts compared with the amount of fatty tissue in the breasts, as seen on a mammogram On a mammography report, breast density is assigned to one of the following four categories— The breasts are almost entirely fatty (about 10% of women)
/why-are-dense-breasts-a-breast-cancer-risk-430657-v1-8493c59449b8433a906c8394895a462c.png)



The Association Between Dense Breasts And Breast Cancer




Study Shows Breast Density Is Most Common Risk Factor For Breast Cancer
More of the breast is made of dense glandular and fibrous tissue (described as heterogeneously dense) This can make it hard to see small tumors in or around the dense tissue Breasts are extremely dense, which makes it hard to see tumors in the tissue Mammogram reports sent to women often mention breast densityA cancerous lump can show up as white on a mammogram Calcifications, which may sometimes be associated with breast cancer or DCIS (ductal carcinoma insitu), also appear white on a Dense breasts can only be determined by having a mammogram reviewed by a radiologist, who will score your breast density as A, B, C or D Dense breasts will have a 'C' ranking meaning the breast tissue is 'heterogeneously dense'



Breast Density What It Is And What It Means To You Mammograms Tomo 3d Mammo Main Line Health




Her Dense Breast Tissue Hid Cancer For Years Now She S Warning Others Cbc Radio
There are four descriptors for breast density on mammography in the 5 th edition of BIRADS 1,2 a the breasts are almost entirely fatty b there are scattered areas of fibroglandular density c the breasts are heterogeneously dense, which may obscure small masses d the breasts are extremely dense, which lowers the sensitivity of mammography C Heterogeneously dense indicates that there are some areas of nondense tissue, but that the majority of the breast tissue is dense About 4 in 10 women have this result About 4 in 10 women have this resultBreasts which are heterogeneously dense, or (D) extremely dense on mammography, are considered "dense breasts" 5 Facts to Know Resources for European Providers Developed by and for health care professionals to advance education on the screening and risk implications of dense breast tissue Learn More



3




Mammography Screening Guidelines Mammogram Guidelines
Now, dense breast tissue is common About twothirds of premenopausal women have dense breasts, and about a quarter of postmenopausal women Put the two together, and about 40% of women have dense breasts Postmenopausal women on hormone replacement therapy tend to have denser breasts For the 10% of women with extremely dense breast tissue (category D), breast cancer risk is about 2 times greater than for women who have scattered fibroglandular density (category B) For women who have heterogeneously dense breasts (category C), the risk of cancer is about 15 times that of a woman with scattered fibroglandular density (category B) D Extremely dense indicates that nearly all of the breast tissue is dense About 1 in 10 women has this result In general, women with breasts that are classified as heterogeneously dense or extremely dense are considered to have dense breasts About half of women undergoing mammograms have dense breasts



1



What Are Dense Breasts Does It Matter
There are scattered areas of density (about 2550 percent), but most of the breast tissue isn't dense Class C (or 3) Heterogeneously dense There is anywhere from 5175 percent dense breast tissue Class D (or 4) Extremely dense Occurs when there is 75 percent or more dense breast tissue This is the highest level of breast density,



Understanding Breast Density Western Missouri Medical Center




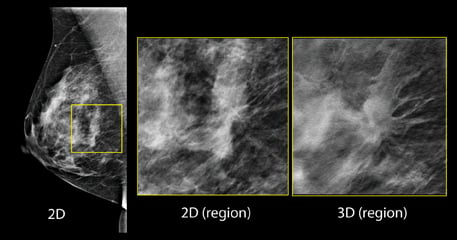
3d Mammo Outperforms Digital Mammo Except In Patients With Extremely Dense Breasts



What Breast Density Means To You Stacey Vitiello M D



Breast Density Breastlink




Knowing Your Breast Density Can Save Your Life Hers Magazine




What Does It Mean To Have Dense Breasts Moffitt




Breast Density Radiology Reference Article Radiopaedia Org



1



Breast Density And Mammogram Reports Dense Breast Tissue




Abbreviated Screening Breast Mri Triad Radiology Associates



Health And Screening Advice For Women With Dense Breasts



Advocating Breast Density Imaging Technology News




Breast Cancer Seattle Cancer Care Alliance



Breast Imaging Big Sky Diagnostic Imaging




Understanding Scattered Fibroglandular Breast Tissue



Get Smart About Dense Breasts Mdedge Obgyn



Dense Breast Tissue What To Know Uva Radiology



Dense Breasts Answers To Commonly Asked Questions National Cancer Institute




Abus For Dense Breasts North Kansas City Hospital North Kansas City Mo




Four Iowa Women Share Their Stories Of Breast Cancer Survival



What Should You Know About Breast Density Breast Cancer Awareness Month Women S Health Research Institute



Dense Breast Tissue What You Need To Know Mayo Clinic Health System




Health Care Provider Faqs Densebreast Info Inc




Forty Eight Year Old With Heterogeneously Dense Breast Tissue Presents Download Scientific Diagram




Dense Breast Tissue



The Problem With Mandatory Breast Density Reporting Laws Scienceblogs




Breast Density Canadian Cancer Survivor Network



Once Dense Always Dense Joan Lunden



Blog How Dense Are You New Research Shows That Not All Dense Breasts Pose An Increased Cancer Risk



The Facts About Breast Density Radiology Associates Of Hartford



Vt Will Require Alerts About Breast Density



Automated Whole Breast Ultrasound Barbara Hayden Dense Breasts



Izotropic Corporation Izotropic Receives Notice Of Allowance For Measuring Breast Density From Us Patent Office



Your Patient Got A Dense Breast Notification With Her Mammogram Report What Are You Supposed To Do Christianacare News




Breast Density And Mammogram Reports Dense Breast Tissue




Dense Breast Tissue And Breast Cancer Risk




Cancer And Breast Density What Are Doctors Withholding The Japan Times



Breast Density In Enid Ok St Mary S Regional Medical Center




Are You Feeling Dense



Breast Density Explained Imaging Technology News




Sixty Eight Year Old With Heterogeneously Dense Breast Tissue Recalled Download Scientific Diagram



Dense Breast Tissue What Is It And Why Should You Care The Mammo Press




Breast Density And Mammogram Reports Dense Breast Tissue



The Radiology Assistant Bi Rads For Mammography And Ultrasound 13




Breast Density What Is It And What Does It Mean For Me Breast360 Org The American Society Of Breast Surgeons Foundation




Breast Density Carolina Breast Imaging Specialists



What Breast Density Means To You Stacey Vitiello M D




Dense Breasts Advocacy Science And Cancer Dr Elisabeth Poorman



Multimodality Imaging Of Breast Parenchymal Density And Correlation With Risk Assessment Springerlink




Breast Density Radiology Reference Article Radiopaedia Org



The Connection Between Dense Breasts And Breast Cancer Patricia Bowden Luccardi



The Importance Of Understanding Your Breast Density Women S Health Blog




Breast Density And Mammogram Reports Dense Breast Tissue




Advice For Breast Cancer Awareness Month Know Your Breast Density Urmc Newsroom



Are You Missing The Added Revenue Of Dense Breast Imaging Radiology Oncology Systems
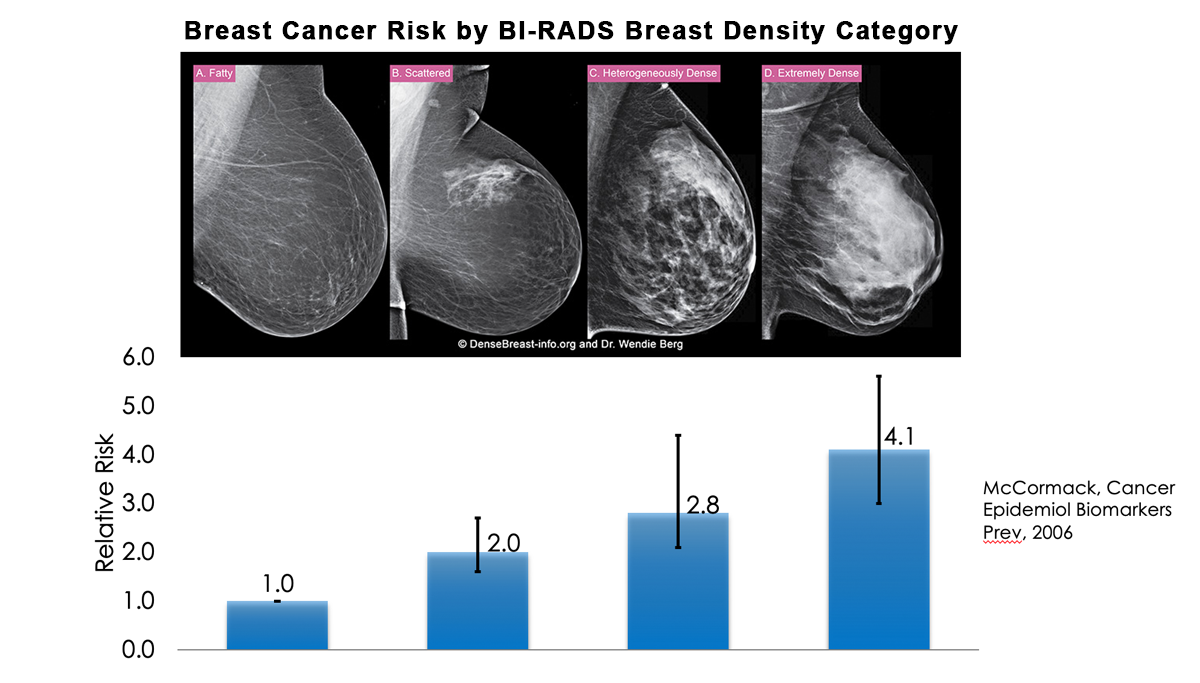



Health Care Provider Faqs Densebreast Info Inc
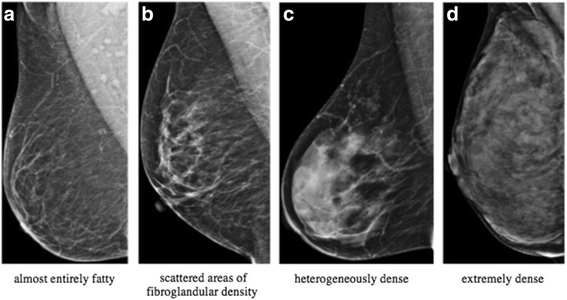



Mammographic Density Changes In Surgical Weight Loss An Indication For Personalized Screening Bmc Medical Imaging Full Text




Three More States Pass Breast Density Notification Bills Imaging Technology News
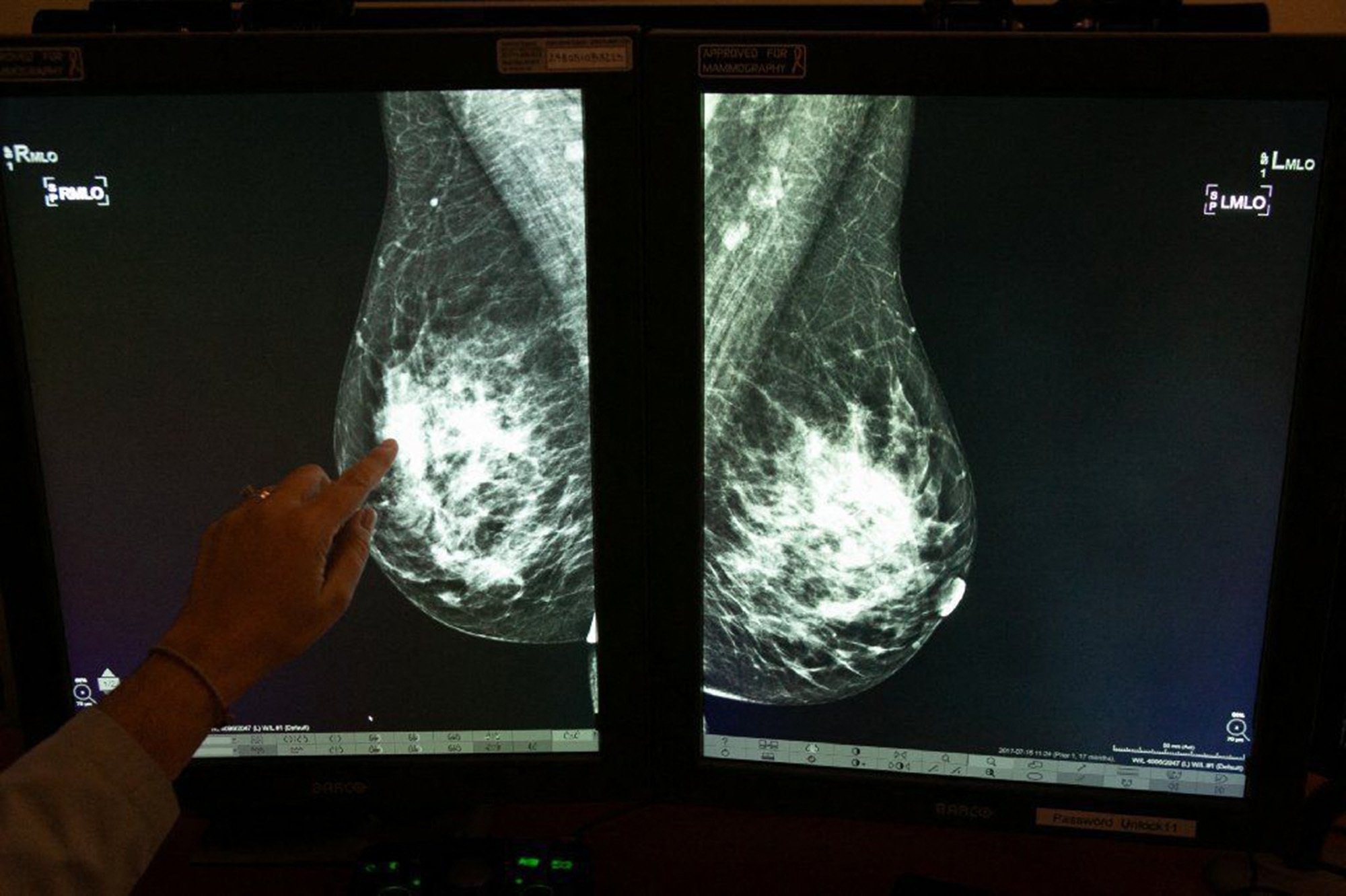



Breast Cancer Faq 8 Things You Should Know About Getting Your First Mammogram Daily Sabah
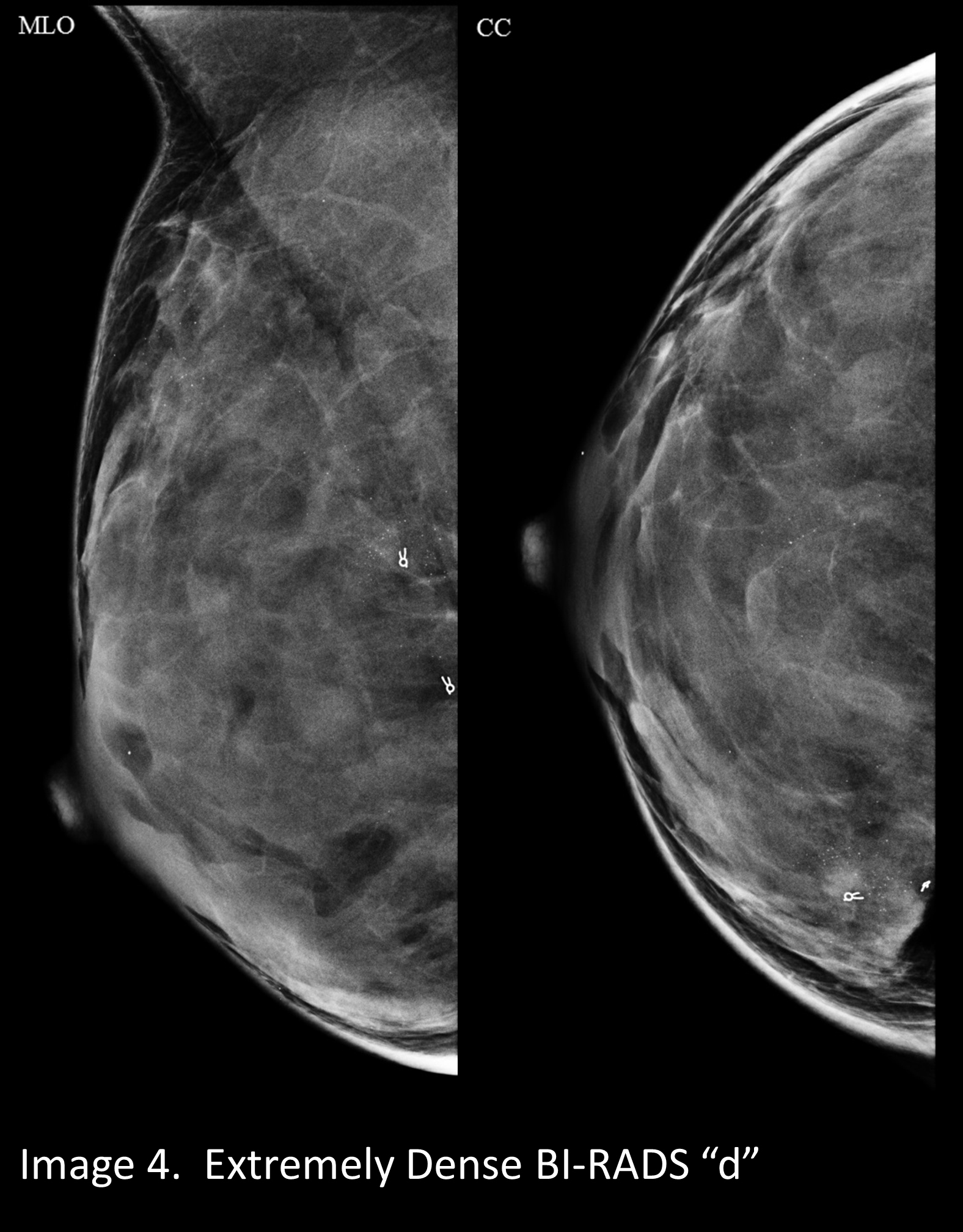



Your Patient Got A Dense Breast Notification With Her Mammogram Report What Are You Supposed To Do Christianacare News




Why Breast Density Matters Prevent Breast Cancer



Breast Density Exam University Radiology Of Nj




Dense Breast Tissue And Automated Breast Ultrasound



Cureus Mammographic Breast Density In Pakistani Women Factors Affecting It And Inter Observer Variability In Assessment



2



Breast Density Bi Rads Classification Moose And Doc



How Dense Are You Dennis R Holmes M D F A C S Breast Cancer Surgeon




Breast Density Cancer What Does It Mean To Have Dense Breasts



Q Tbn And9gcqybnohlifjvcf2elp Bltnoj94yb7 B6tbcn Jidbtkw3brt1t Usqp Cau



Molecular Breast Imaging Snmmi




The Difference Between Dense And Nondense Breast Tissue Article Community Care Physicians P C




Mammogram Imaging Of The Left Breast A The Right Craniocaudal View Download Scientific Diagram



Dense Breast Tissue What It Means To Have Dense Breasts Mayo Clinic




Screening Ultrasound As An Adjunct To Mammography In Women With Mammographically Dense Breasts American Journal Of Obstetrics Gynecology



How To Decrease Breast Density To Reduce Breast Cancer Risk Mammalive Foundation



Breast Density Why Is It Important Lake Medical Imaging The Villages Florida



Fibroglandular Densities Mammographic Breast Density Itn




The Evolution Of Breast Density Scales And Algorithms Densitas



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿